|
Northern Ontario Plant Database 
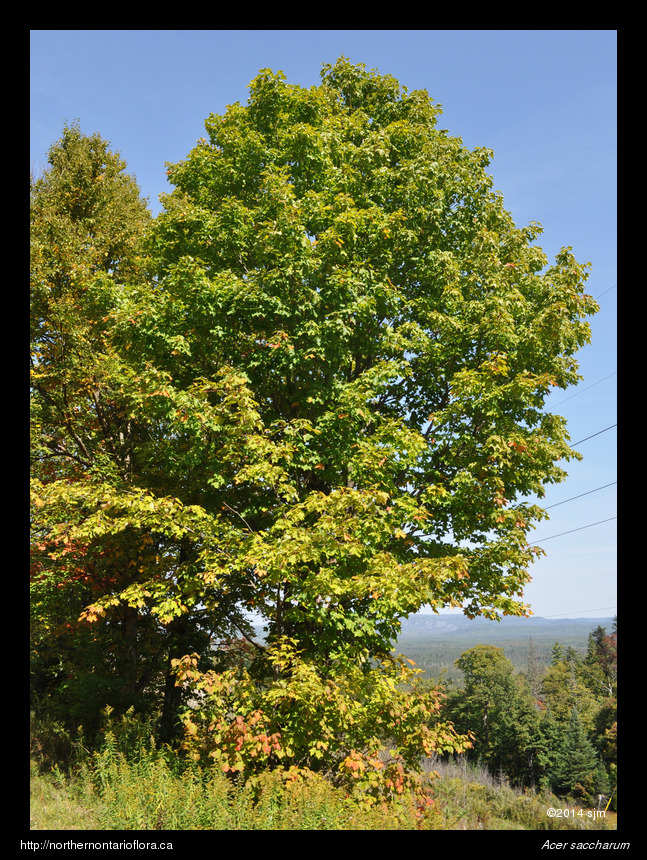
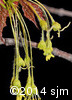
Plant DescriptionAcer saccharum MarshallEn: sugar maple, hard maple, rock maple, bird's-eye maple
Sapindaceae (Soapberry Family) General: A medium-sized to large hardwood tree, to 35 m tall, branches spreading; twigs reddish brown to green, smooth (glabrous); bark gray and smooth in young trees, darker, scaly, and deeply furrowed in older trees; terminal buds brown, cone-shaped (conical), to 1.2 cm long, sharply pointed (acuminate), with 6-8 pairs of slightly hairy, overlapping (imbricate), bud scales. Leaves: Opposite, simple, petiolate, the petiole to 8 cm long; leaf blade palmately lobed, to 20 cm wide, usually 5 lobed, each lobe shouldered, with 1-2 pairs of large, pointed teeth placed below the sharply pointed (acuminate) apex; upper surface dark green, lower leaf surface pale; leaf base somewhat cordate; margins entire between the few coarse, acuminate teeth of each lobe. Leaves turn yellow, then vivid orange and red in the Autumn. Flowers: Small, clustered, pendulous; pedicels pubescent, to 10 cm long; calyx 5-lobed, greenish-yellow, tubular, 4-6 mm long; petals absent; flowers have both stamens and pistils but only one sex will be functional; fertile male flowers will have 4-12 stamens; fertile female flowers will have a 2-carpellate, superior ovary with 2 long and slender styles; flowers emerge with the leaves in spring. Fruits: A pair of winged samaras, to 2.5-4 cm long, single-seeded; wings slightly divergent; fruits mature in Autumn. Habitat and Range: Acer saccharum occurs on rich, moist, well-drained soils in deciduous forests. It is native to eastern North America, ranging from Nova Scotia to eastern Manitoba and upland regions of the southeastern U.S. Sugar maple is the dominant tree throughout much of the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence forest region; in Ontario, it occurs as far north as Lake Nipigon (Scoggan 1978). Similar Species: Acer rubrum (red maple) can be distinguished by its serrated leaf margins; the leaves turn scarlet, often mottled with yellow, in the Autumn. Acer saccharinum (silver maple) has more deeply lobed leaves with coarsely serrate margins and a more strongly whitened lower surfaces; the leaves turn yellow in Autumn. Internet Images: The Acer saccharum webpage from Walter Muma's website Ontario Trees and Shrubs. The Acer saccharum webpage from the Trees of Wisconsin website. - written by Derek Goertz Back to species list |
||||||||||||||||||||||